Have you ever wondered what does the world look like through the eyes of a bee? If you have, you are not alone. Biologists have been pondering this question for a long time, and now we have sufficient knowledge about the physiology of the bee to understand exactly what they see.
If you like this article then why not check out our article on Can Wasps See in Color? The surprising answer
To understand what a bee sees through its eyes, it’s necessary to answer the most basic question first – can bees see color? Yes, bees can see color, to extent, but their vision is different than human color vision. They can distinguish between green, blue, and ultraviolet light, but they can’t distinguish red from black.
How exactly does bee vision differ from the human vision? How many eyes does a bee have? Why do bees see ultraviolet light? Read on if you want to find out the answers to these questions and more.
If you are interested in learning more about how to cultivate your garden to be friendly to bees and other insects or the basics of becoming a beekeeper, checkout our online course recommendations here.
Table of Contents
What do Bees See?
To understand what colors bees see, we need to take a moment to think about human vision. How do we see colors? When we see a colored object, what we actually see is light reflected from this object. The light is reflected at different wavelengths, and this determines the color we see.
All of the colors we see are the combination of three basic colors – red, blue and green. In more scientific terms, humans can distinguish between wavelengths from approximately 390 to about 750 nanometers. The colors we can see fall into this range on the color spectrum.
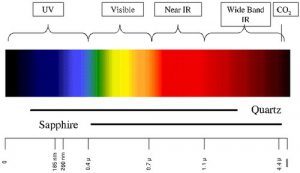
Bees, on the other hand, see wavelengths ranging from approximately 300 to 650 nanometers. Because of this, they don’t see the color red, it’s outside their vision spectrum. However, they see one color we can’t – ultraviolet, which is very important for bees (more on this later). Just like we see the combination of red and blue as purple, for example, bees see a range of different colors. Among those, they can see a color called “bee’s purple”, a combination of yellow and ultraviolet – something we can’t even imagine. The ability to see ultraviolet and polarized light helps bees make sense of the world around them, and find flowers with great accuracy.
Bees are partially color-blind when compared to us, since they can’t see red. However, we are also partially color-blind when compared to bees – since we can’t see ultraviolet! Bee vision is also much faster than our vision. What this means is that bees can see fast moving objects much better than we can, so they can easily distinguish between different objects such as varieties of flowers while flying.
The Honey Bee and Its Eyes

How many eyes does a bee have? If you are thinking two, you are actually wrong. Bees have five eyes. That’s right, five! When you look at a bee, you’ll see two large eyes on the side of its head. Those are her large compound eyes. Bees also have three small eyes on the top of their heads. So how do bees use their five eyes to see the world around them? Let’s start with the big compound eyes.
The large eye of the bee contains more than 4000 individual lenses that are shaped like a hexagon. Scientifically, these lenses are called ommatidia. Each of these lenses contains a cluster of photoreceptor cells, surrounded by other types of cells. These photoreceptors allow bees to see light and, therefore, color. Now, bees are trichromatic, just like humans. This means they have three types of photoreceptor cells for three different colors – blue, green, and ultraviolet. All the color combinations they see are based on those three colors.
Now, all of these small ommatidia work together to create an image that a bee sees. For comparison – a human eye has around 1.5 million of photoreceptors, which means that the clarity of a bee’s vision is much worse than ours. In fact, they need to be quite close to an object to see it clearly.
So far we have only talked about the bee’s two large eyes, but a bee is also equipped with three small eyes located on the top of its head. These eyes are called ocelli and their structure is quite simple. Many other insects have this type of eye, including ants, wasps, dragonflies, and grasshoppers. These simple eyes don’t actually produce visual images, but they allow bees to detect levels of light in a very sophisticated manner. It is believed that these small ocelli help bees navigate during flight, and stay oriented by judging the intensity of light.
Another fun fact about bees’ eyes – bees actually have hairy eyes! Tiny hairs grow on the two of their large compound eyes.
Other weird facts about bees can be found here on our 50 shocking facts article.
How Do We Know That Bees See Color?
Almost a hundred years ago, a Nobel Prize-winning scientist Karl von Frisch was investigating the perception and behavior of bees. He was the first to prove that bees can see color, and he did so with a very simple experiment, that you can try for yourself too.
So what did he do? He took two identical pieces of blue paper and put a couple of drops of honey on one of them. Bees landed on the paper with honey, filled their stomachs with it, and went back to the hive. After a couple of minutes, they would return. After this action was repeated a couple of times, the scientist removed the paper with honey.
In its place, he put down two identical pieces of paper, only one was blue and one was red. None of them contained honey. The bees kept gathering on the blue paper, even though there was no honey on it. This not only proves that bees can distinguish between colors, but also that they remember which paper contained honey.
However, this does not provide definitive proof that bees see color. If their vision was in greyscale, they would still distinguish between blue and red, only they would appear as different shades of grey – simply distinguishable by the level of brightness. For this reason, Karl von Frisch tried another test. He placed a whole range of grey papers, ranging from white to black on a table, along with one blue paper. Bees that previously learned that blue papers contain honey, still landed on the blue paper, which means that they can, in fact, see color, and not just levels of light. However, when the same thing was done with a red paper, bees could not distinguish between the grey and the red. This is how we learned that bees cannot see the color red.
Today, of course, we have much more detailed information about how bees see the world around them. For example, a group of scientists at Monash University in Australia created a device that recreates the way a bee’s eye works. The device was constructed from 4.500 black drinking straws. This helped them realize how flowers look like to bees, and also how they navigate through their surroundings.
The Importance of Ultraviolet Vision in Honey Bees

You probably know that bees are very important for our ecosystem. A huge number of plants, in general, and commercially grown crops, specifically, need bees to pollinate them in order to survive. But how do bees find flowers they need to pollinate? Besides the sense of smell, their vision is the most important guide. Furthermore, the way bees see flowers is different from the way we see them. In fact, many flowers have ultraviolet patterns on them. These patterns help bees gather the nectar (if you want to find out how flowers look from a bee’s point of view, check out our collection of images showing how bees see the world article. Many flowers have a “bull’s eye” pattern that helps bees find the source of nectar easily. For this reason, ultraviolet vision is incredibly important to bees, and not only to bees, but it’s also what keeps whole ecosystems functioning!
Related Questions
What color can bees not see?
Even though bees can see a range of colors, they cannot see the color red. This is because their eyes are constructed differently than human eyes. While we see colors as combinations of blue, green, and red, bees see combinations of blue, green, and ultraviolet.
Why do bees see ultraviolet light?
Many flowers contain ultraviolet patterns that humans can not see. However, for bees, these patterns are very important because they help them find the source of nectar. Bees see ultraviolet light because it helps them find the flowers to pollinate.
Can bees see in the dark?
No, bees cannot see in complete darkness. European honey bees forage during the day and return to their hives at night. However, some species, like Africanized honey bees actually forage at night. The inside of the hive is also very dark, and bees conduct complex activities inside the hive. However, they rely more on the senses of touch and smell while they are in the hive.
If you like this article then why not check out our article on Can Wasps See in Color? The surprising answer
Sources:
Von Frisch, Karl. The dancing bees. Harcourt, Brace, 1955.
Evans, Elizabeth, and Carol A. Butler. Why Do Bees Buzz?: Fascinating Answers to Questions about Bees. Rutgers University Press, 2010.
